Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Klotz, S.*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Kunc, K.*; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori
Physical Review B, 95(17), p.174111_1 - 174111_7, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:81.94(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The compression behaviour of deuterated ice VII and VIII was investigated by high pressure neutron scattering in the pressure range 2-13.7 GPa between 93 K and 300 K. We establish equations-of-state which contain accurate values for the bulk moduli B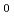 , their pressure derivatives B'
, their pressure derivatives B'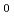 , as well as the ambient pressure volumina V
, as well as the ambient pressure volumina V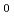 . These equations-of-state hold over a large part of the stability domain of ice VII, by comparison with available X-ray data, and to at least
. These equations-of-state hold over a large part of the stability domain of ice VII, by comparison with available X-ray data, and to at least  13 GPa for ice VIII. They are indistinguishable at low pressures, but beyond
13 GPa for ice VIII. They are indistinguishable at low pressures, but beyond 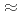 7 GPa and at low temperatures ice VIII appears to become stiffer than expected. This might be related to an anomalous phonon hardening observed previously in ice VIII in this
7 GPa and at low temperatures ice VIII appears to become stiffer than expected. This might be related to an anomalous phonon hardening observed previously in ice VIII in this  range [D.D. Klug et al., Physical Review B, 70, 144113 (2004)].
range [D.D. Klug et al., Physical Review B, 70, 144113 (2004)].
Klotz, S.*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Pietrucci, F.*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Ludl, A.-A.*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Bove, L. E.*
Scientific Reports (Internet), 6, p.32040_1 - 32040_8, 2016/08
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:59.92(Multidisciplinary Sciences)It has been known since decades that certain aqueous salt solutions of LiCl and LiBr readily form glasses when cooled to below  160 K. This fact has recently been exploited to produce a
160 K. This fact has recently been exploited to produce a  salty
salty high pressure ice form: When the glass is compressed at low temperatures to pressures higher than 4 GPa and subsequently warmed, it crystallizes into ice VII with the ionic species trapped inside the ice lattice. Here we report the extreme limit of salt incorporation into ice VII, using high pressure neutron diffraction and molecular dynamics simulations. We show that high-pressure crystallization of aqueous solutions of LiCl
high pressure ice form: When the glass is compressed at low temperatures to pressures higher than 4 GPa and subsequently warmed, it crystallizes into ice VII with the ionic species trapped inside the ice lattice. Here we report the extreme limit of salt incorporation into ice VII, using high pressure neutron diffraction and molecular dynamics simulations. We show that high-pressure crystallization of aqueous solutions of LiCl 5.6H
5.6H O and LiBr
O and LiBr 5.6H
5.6H O leads to solids with strongly expanded volume, a destruction of the hydrogen-bond network with an isotropic distribution of water-dipole moments, as well as a crystal to-amorphous transition on decompression. This highly unusual behavior constitutes an interesting pathway from a glass to a crystal where translational periodicity is restored but the rotational degree of freedoms remaining completely random.
O leads to solids with strongly expanded volume, a destruction of the hydrogen-bond network with an isotropic distribution of water-dipole moments, as well as a crystal to-amorphous transition on decompression. This highly unusual behavior constitutes an interesting pathway from a glass to a crystal where translational periodicity is restored but the rotational degree of freedoms remaining completely random.
Yokoya, Akinari; Fujii, Kentaro; Narita, Ayumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fujii, Kentaro; Izumi, Yudai; Narita, Ayumi; Yokoya, Akinari; Herv du Penhoat, M.-A.*; Touati, A.*; Vuilleumier, R.*; Gaigeot, M.-P.*; Politis, M.-F.*
du Penhoat, M.-A.*; Touati, A.*; Vuilleumier, R.*; Gaigeot, M.-P.*; Politis, M.-F.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Izumi, Yudai; Matsuo, Koichi*; Fujii, Kentaro; Yokoya, Akinari
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fujii, Kentaro; Izumi, Yudai; Narita, Ayumi; Yokoya, Akinari; Herv du Penhoat, M.-A.*; Ghose, K.*; Vuilleumier, R.*; Gaigeot, M.-P.*; Politis, M.-F.*
du Penhoat, M.-A.*; Ghose, K.*; Vuilleumier, R.*; Gaigeot, M.-P.*; Politis, M.-F.*
no journal, ,
In order to reveal a role of hydration water on the destruction of dR molecule induced by core electron ionization, we measured a mass spectrum of desorbed ions from the hydrated dR film exposed to soft X-rays with energy above oxygen K-shell ionization threshold (560 eV). The spectral changes of X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) of the films after the soft X-ray exposures were also examined the chemical structure of the irradiation products. The yield of the desorbed ions, which were produced by the destruction of furanose ring structure, obviously decreased with depositing one layer of water molecules on the film. This result suggests that the hydration water layer on dR film suppresses an intense destruction of the furanose ring structure of dR induced by the core ionization, or the desorption of the resulting fragment ions from the sample film. We also observed new peaks emerging around 534-536 eV in the XANES spectrum of the hydrated sample irradiated. These new peaks are located at the similar energies to those of XANES peaks of formic acid. The hydration water could also contribute to produce the newly forming products containing a carboxyl group.
Fujii, Kentaro; Izumi, Yudai; Narita, Ayumi; Yokoya, Akinari; Herv du Penhoat, M.-A.*; Ghose, K.*; Vuilleumier, R.*; Gaigeot, M.-P.*; Politis, M.-F.*
du Penhoat, M.-A.*; Ghose, K.*; Vuilleumier, R.*; Gaigeot, M.-P.*; Politis, M.-F.*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Fujii, Kentaro; Izumi, Yudai; Krishna, G.*; Pablo, L.-T.*; Alain, T.*; Rodolphe, V.*; Marie-Pierre, G.*; Marie-Francoise, P.*; Marie-Anne, H.*; Yokoya, Akinari
no journal, ,
In order to reveal the role of hydration water regarding ionization the constituent atoms, we measured a mass spectrum of ions desorbing from hydrated deoxyribose (dR) films exposed to monochromatic soft X-rays (560 eV). Desorbing positive ions were detected by a quadrupole mass spectrometer to examine the effect of Coulomb explosion of valence holes produced as a result of Auger decay after the ionization. The yield of desorbing ions which were produced by the destruction of the furanose ring structure of dR, obviously suppressed when one layer of water molecules was deposited onto the film. This result suggests that the hydration water layer on the film inhibits the intense destruction of the furanose induced by the ionization of K-shell electrons of oxygen, or the desorption of the resulting fragment ions from the sample film.